OCS-TGBM: Intelligent Analysis of Organic Chemical Synthesis Based on Topological Data Analysis and LightGBM
In MATCH-COMMUNICATIONS IN MATHEMATICAL AND IN COMPUTER CHEMISTRY, 2024
Introduction
Organic synthesis has been widely used in drug discovery and development. The intelligent yield prediction and analysis of high-throughput coupling reaction is one of the vital and challenging research hotspots in the field of organic synthesis. However, the existing methods focus on intelligent prediction rather than study and interpret the internal relationship between reaction conditions and yield. For tackling this problem, we propose OCS-TGBM, an intelligent organic synthesis analysis model by combining topological data analysis (TDA) and Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM). OCS-TGBM can deeply explore the internal relationship between reaction conditions and yield, and obtain high-yield reaction conditions and combinations. In order to further enhance the generalization of OCS-TGBM, we also design a stratified diversity sampling strategy for LightGBM in the training stage based on TDA clustering. Experimental results show that the OCS-TGBM model is superior to other methods in analyzing and predicting the reaction performance of high-throughput organic synthesis. And it provides intelligent assistance for the optimal design of the reaction system and the evaluation of reaction conditions, thus greatly accelerating the process of the drug discovery and development.
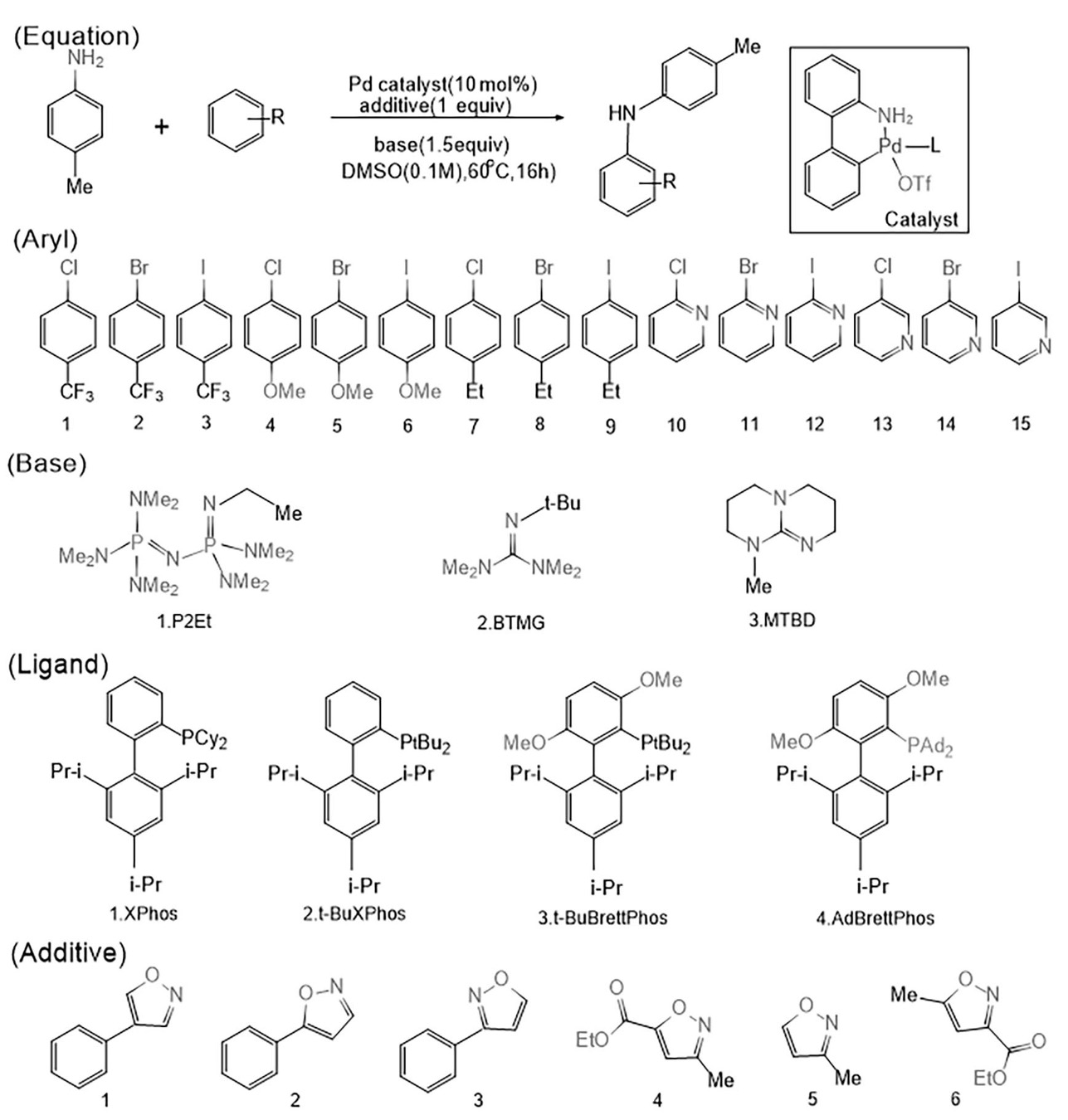
Figure 1. Some reactants of Buchwald-Hartwig amination reaction.
Method
1. Topological Data Analysis and Multi-Factor Analysis of Variance
- Cluster various reaction conditions and the corresponding yield mean based on topological data analysis, identifying more high-yield conditions.
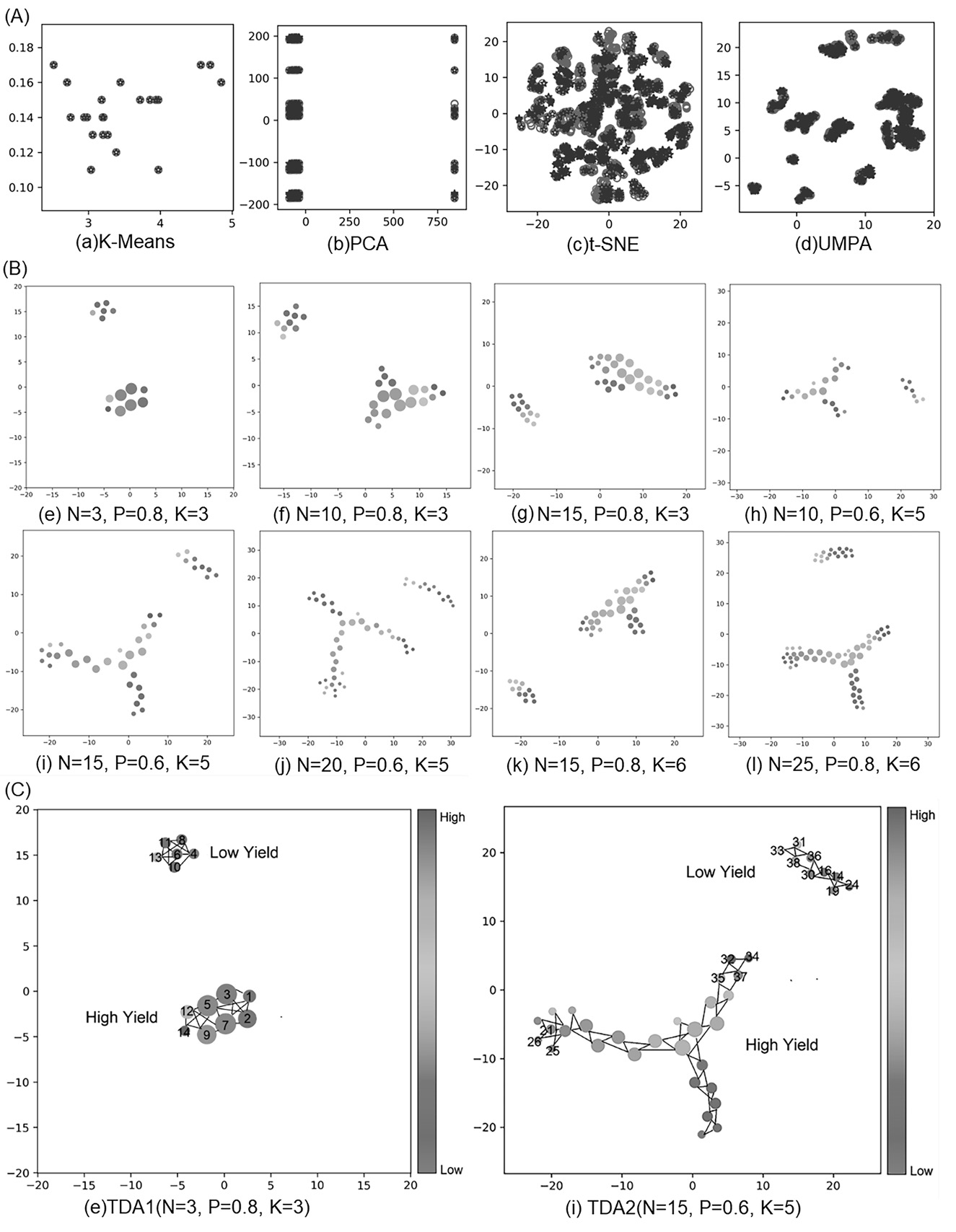
Figure 2. Cluster visualization.
- Analyze the combination effects of additives, aryls, bases and ligands on yield based on multi-factor analysis of variance, identifying the optimal combination of reaction conditions.
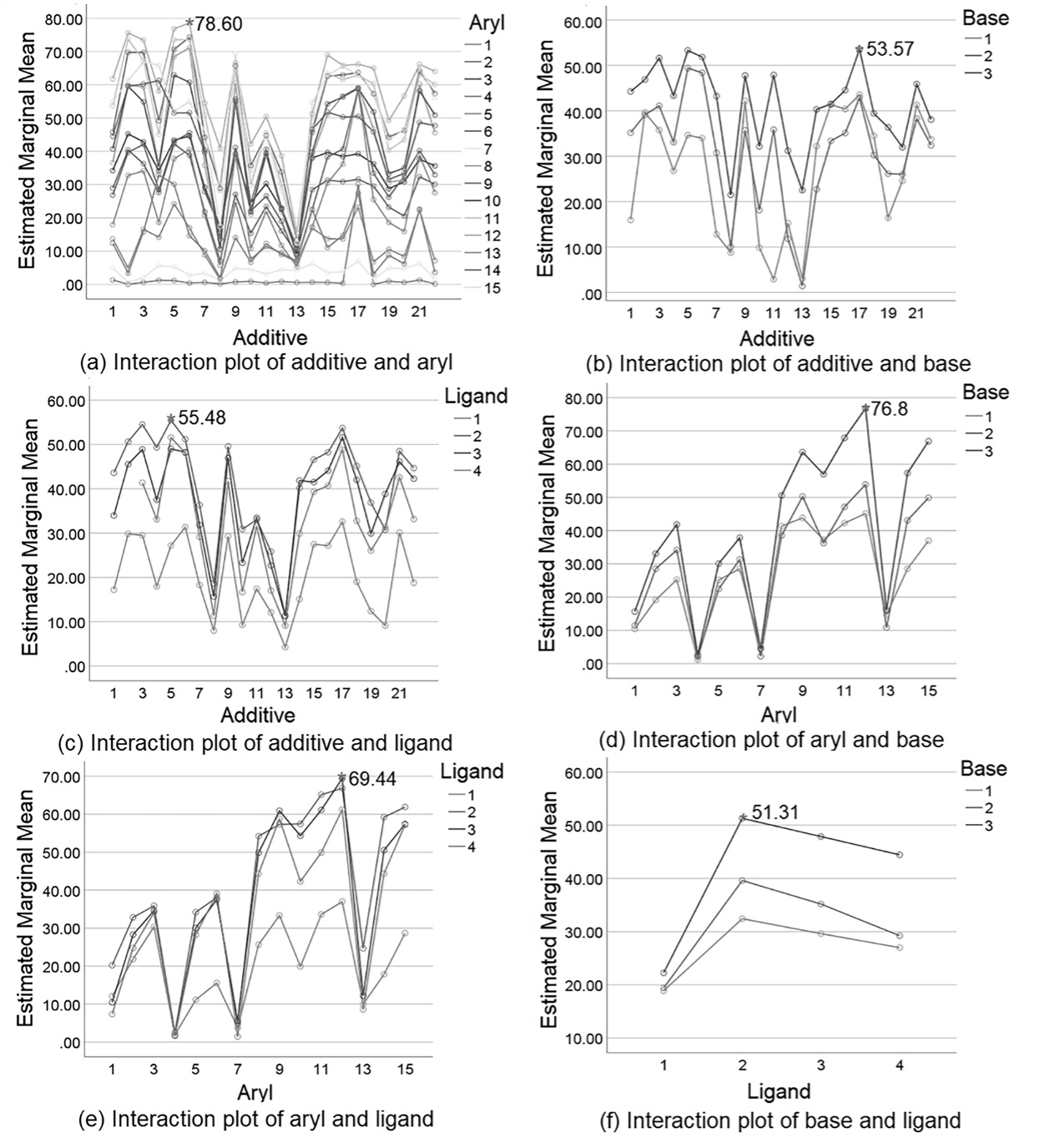
Figure 3. Pairwise interaction plot of additive, aryl, base, ligand.
2. LightGBM for Yield Prediction
- Learning rate setting by cross-validation and grid search.
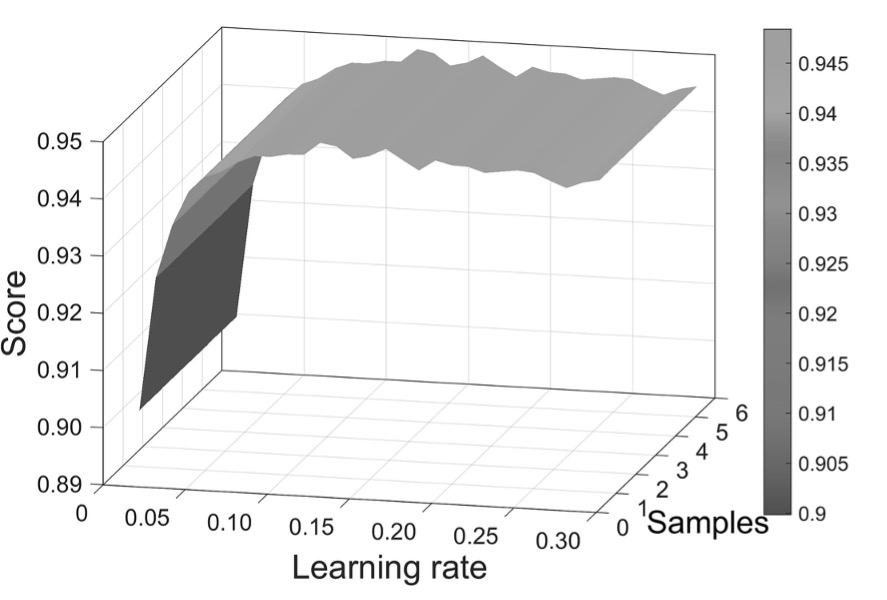
Figure 4. Grid search for learning rate.
- Superior yield prediction accuracy and speed compared to other methods.
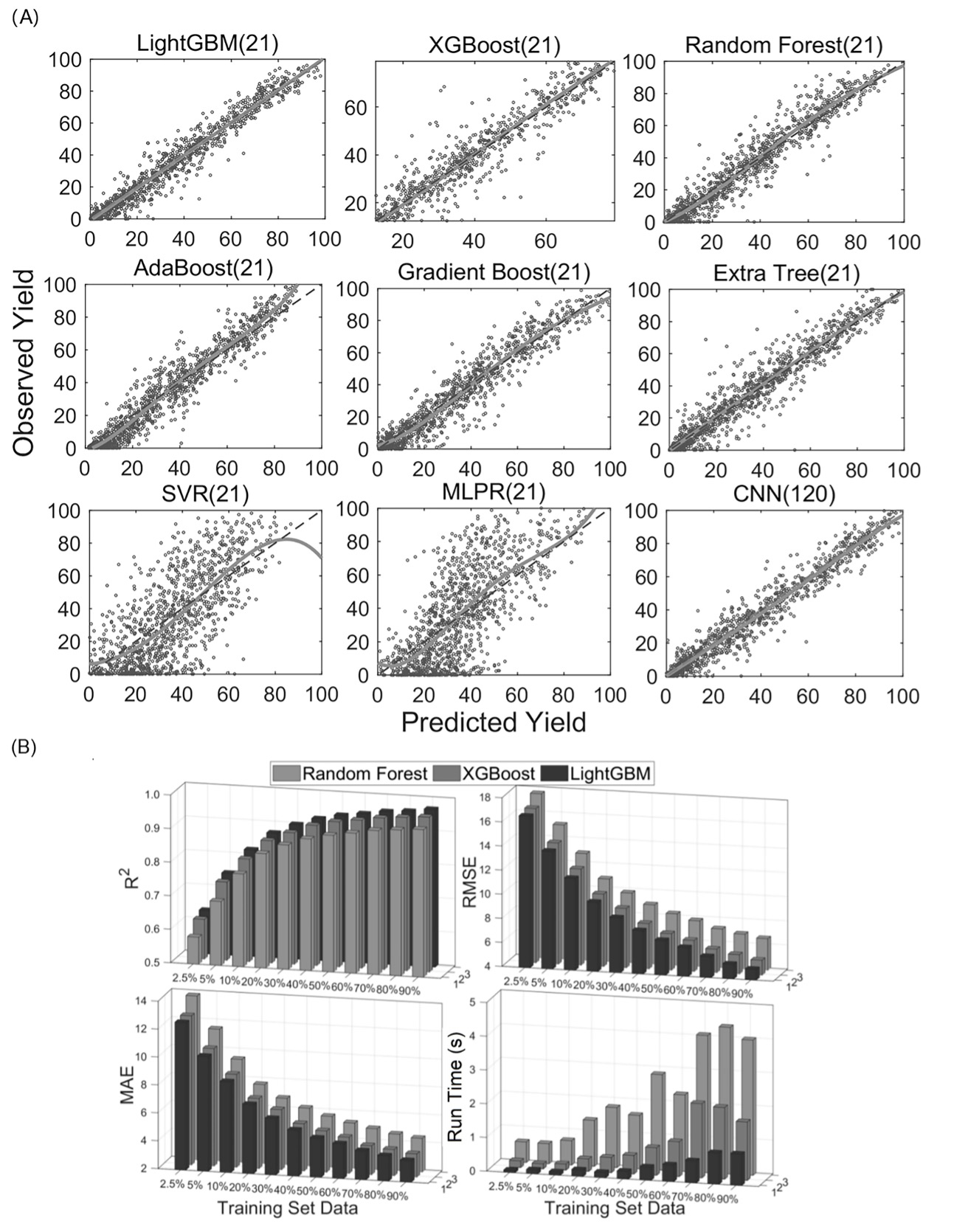
Figure 5. Prediction performances of different models.
3. Stratified Diversity Sampling
Stratified diversity sampling combines the advantages of stratified sampling (ensure coverage of all categories) and diversity sampling (increase variation in the training set). It is used to sample the training samples in the training stage, improving the representativeness and out-of-fold generalization of OCS-TGBM. The sampling steps are as follows:
(1) Based on TDA clustering, the dataset is divided into several strata (layers or categories). For each layer, randomly select 10% of the data as the initial labeled set, and assign the remaining 90% as unlabeled.
(2) For each unlabeled data point, calculate the cosine similarity with all labeled data points:
\[\cos(\theta) = \frac{\sum_{k=1}^{n} x_{1k} x_{2k}}{\sqrt{\sum_{k=1}^{n} x_{1k}^2} \cdot \sqrt{\sum_{k=1}^{n} x_{2k}^2}},\]where \(x_{1k}\) represents the labeled sample, and \(x_{2k}\) the unlabeled sample.
(3) Sort the similarity values of each unlabeled sample to the labeled set in ascending order (i.e., least similar samples come first).
(4) Choose the top-𝑚 most dissimilar unlabeled samples and add them to the labeled set. Remove these samples from the unlabeled set.
(5) Repeat steps (2)-(4) until the labeled set reaches n% of the total data. The labeled set \((A \times n\%)\) becomes the training set, and the unlabeled set \((A \times (1 - n\%))\) becomes the testing set.
